Take Advantage of Limited-Time Offers on Luxury Homes with Stunning Features!
Discover Your Dream Home with Our Latest Listings and Personalized Services!
Join Us for Exclusive Open House Events This Weekend and Find Your Perfect Home!
The Indian realty sector is amongst the largest revenue contributors to the country's economy. Yet, it is also greatly affected by government policies and regulations. During the past few decades, several reforms have been rolled out in order to introduce transparency, increase investments, and provide protection to consumers. In this blog, we shall cover the key government policies impacting Indian real estate and their consequences on the market.

Enacted in 2016, RERA was brought into force to bring more transparency and accountability to the real estate industry. According to this act, real estate developers are required to register their projects under RERA and provide crucial information such as project completion dates and financial statements. Due to this, homebuyers are now protected by law from fraud and project delays. Also, developers must deposit 70% of the project money in an escrow account, guaranteeing effective use of funds. RERA has enhanced consumer trust, and the real estate market is now more organized and reliable.
GST, which was introduced in 2017, revolutionized the tax structure of real estate drastically. In this system, a uniform tax rate substituted various indirect taxes such as VAT, service tax, and excise duty. GST is now levied at 5% for properties under construction and 1% for affordable housing projects. Yet, ready-to-move-in homes are exempted from GST. Although GST has made taxation simpler, it has also raised expenses for developers, which has resulted in higher prices for properties in certain segments. Even though there is a challenge initially, the efficient tax structure profits buyers and builders in the long term.
Initiated in 2015, the PMAY scheme targets affordable housing for all by 2022. Through this program, the government provides subsidy on home loans for economically weaker sections (EWS), lower-income groups (LIG), and middle-income groups (MIG). The scheme has motivated first-time homebuyers, especially in urban and semi-urban centers. It has also increased demand for affordable housing projects, which has resulted in more construction in this sector.
The government of India has permitted 100% FDI in the real estate sector, drawing high foreign investment. The policy has resulted in the construction of mega infrastructure projects, commercial property, and smart cities. The influx of foreign funds has raised the quality of construction, adopted world-class best practices, and made the industry overall more competitive. India's real estate industry is now a very attractive place for both national and international investors to invest in.
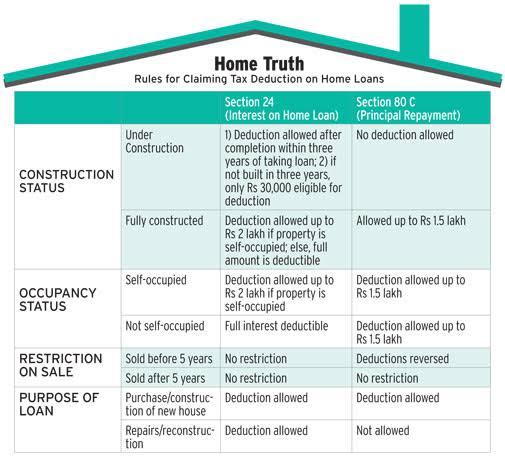
To encourage housing for all, the government has launched various tax concessions for house buyers. Repayment of principal amount of a home loan is deductible under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act up to ₹1.5 lakh per annum. Besides this, repayment of home loan interest is deductible under Section 24(b) up to ₹2 lakh per annum. These tax concessions make home ownership a worthwhile proposition and offer relief to buyers by letting them claim deductions, thus making property a good long-term investment.
The Smart Cities Mission, which was initiated in 2015, focuses on building 100 smart cities with updated infrastructure, digital government, and better urban planning. The project has spurred more real estate development in aspiring cities as it encourages investment in commercial and residential spaces. With developing smart cities, real estate values in such locations are bound to increase, making it advantageous for both investors and buyers.
Demonetization of ₹500 and ₹1,000 denomination currency notes in 2016 had a short-term adverse effect on real estate deals, especially in resale and luxury property segments. But in the long term, it brought down black money circulation and boosted transparency in property transactions. The action also promoted digital payment and banking transactions in real estate, resulting in a more organized and formalized sector.
The Model Tenancy Act was enacted in order to reconcile the interests of landlords and tenants and make the rental market more efficient. The law offers well-defined rules relating to security deposits, rent agreements, and eviction. The act is likely to increase the demand for rental housing, especially in cities, as more property owners are likely to let out their homes without risking legal issues.
Government policies greatly influence the Indian real estate sector. Though certain changes, such as RERA and GST, have enhanced transparency, others, such as PMAY and tax sops, have reduced the cost of housing. The overall impact of these policies is a more organized and investor-friendly real estate industry. Familiarity with the measures can assist homebuyers, investors, and builders in making well-informed decisions in the changing real estate scenario.
The growth of smart cities in India is revolutionizing urban spaces and redefining the real estate industry. This blog discusses how smart city projects are impacting urban real estate, with a focus on the advantages for investors, developers, and residents.
The Indian real estate market in 2025 is witnessing significant shifts across residential, commercial, and retail sectors. This blog delves into the latest trends, including housing affordability, luxury property demand, office space expansion, and the rise of suburban developments, providing...